Gender Based Violence and implications
What is Gender Based Violence
Gender-based violence is a general term used to capture any type of violence that is rooted in exploiting unequal power relationships between genders. This can include gender norms and role expectations specific to a society as well as situational power imbalances and inequities. Gender-based violence can impact anyone, and can include intimate partner and family violence, elder abuse, sexual violence, stalking and human trafficking.
Elder abuse is any action that causes harm or distress to an older person. Elder abuse occurs within the context of trusting familial or care-taking relationships, and can include neglect as well as threats or the actual use of physical, sexual, emotional, verbal, psychological, or financial abuse. "Elder" or "older adult" typically refers to individuals aged 60+.
Sexual violence is any action that results in the loss or removal of sexual autonomy for a person. Sexual violence includes sexual harassment, sexual assault, sex trafficking, non-consensual distribution of intimate images, and any other non-consensual, forced, or drug-facilitated sexual action.
Stalking is a pattern of harassing behavior or course of conduct directed at a specific person that would place that person in reasonable fear. Stalking behaviors include, but are not limited to, monitoring someone’s activities, following someone, leaving unwanted gifts and notes, and making repeated phone calls to someone and/or their family, friends, or workplace.
Human trafficking is the use of power and control to force, defraud or coerce someone into engaging in labor or services, including commercial sex. Traffickers use tactics including violence, emotional manipulation, and psychological threats, exploiting social and economic inequity for their benefit
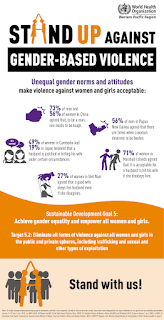
Gender-based violence (GBV) is widespread around the world, in rich societies and in poor. It can take many different forms: physical, sexual, emotional, and economic. Gender-based violence takes places in homes, communities, schools, and workplaces. While no single person should have to experience violence, the evidence shows that GBV is widespread.
Socio economic impact of Gender Based Violence
Gender-based violence has significant socio-economic implications, including:
1. **Healthcare Costs**: Victims of gender-based violence often require medical attention, leading to increased healthcare costs. This burden can strain healthcare systems and lead to higher insurance premiums.
2. **Lost Productivity**: Survivors may miss work due to injuries or psychological trauma, resulting in lost productivity for both individuals and businesses. This can hinder economic growth.
3. **Reduced Workforce Participation**: Fear of violence can discourage women from participating in the workforce, limiting their economic opportunities and potential contributions to society.
4. **Educational Impact**: Gender-based violence can disrupt education, particularly for girls. This can lead to reduced educational attainment, limiting future job prospects and earning potential.
5. **Psychological Consequences**: Survivors often suffer from mental health issues, which can lead to reduced quality of life and increased demand for mental health services.
6. **Increased Social Services**: Communities and governments must allocate resources to address the aftermath of gender-based violence, including shelters, counseling services, and legal support.
7. **Economic Inequality**: Gender-based violence perpetuates gender inequality by limiting women's economic opportunities and reinforcing traditional gender roles.
8. **Long-Term Economic Costs**: These implications can have long-term economic consequences for individuals and societies, as they perpetuate cycles of poverty and inequality.
Addressing gender-based violence is not only a moral imperative but also crucial for promoting social and economic development, as it contributes to a more equitable and prosperous society.
.png)
.png)
Comments
Post a Comment